Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- Queue
- typeORM
- Bull
- 공룡게임
- Dinosaur
- JavaScript
- nestjs
- AWS
- 정렬
- flask
- MySQL
- TypeScript
- game
- react
- OCR
- jest
- Python
- Sequelize
- 게임
- MongoDB
- nodejs
- class
- mongoose
- Express
- 자료구조
- dfs
- Nest.js
- cookie
- GIT
Archives
- Today
- Total
포시코딩
힙(Heap) 본문
728x90
힙(Heap)
데이터에서 최대값과 최소값을 빠르게 찾기 위해 고안된 완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree)
* 완전 이진 트리: 노드를 삽입할 때 최하단 왼쪽 노드부터 차례대로 삽입하는 트리
- 배열에 데이터를 넣고, 최대값과 최소값을 찾으려면 O(n)이 걸림
- 이에 반해, 힙에 데이터를 넣고 최대값과 최소값을 찾으면 O(logn)이 걸림
- 우선순위 큐와 같이 최대값 또는 최소값을 빠르게 찾아야 하는 자료구조 및 알고리즘 구현 등에 활용됨
우선순위 큐
import queue
data_queue = queue.PriorityQueue()
data_queue.put((10, "korea"))
data_queue.put((5, 1))
data_queue.put((15, "china"))
print(data_queue.get()) # (5, 1)
print(data_queue.get()) # (10, 'korea')
print(data_queue.get()) # (15, 'china')
분류
- 최대 힙(Max Heap): 최대값을 구하기 위한 구조
- 최소 힙(Min Heap): 최소값을 구하기 위한 구조
구조(조건)
- 각 노드의 값을 해당 노드의 자식 노드가 가진 값보다 크거나 같다. (최대 힙의 경우)
* 최소 힙의 경우 반대로 각 노드의 값은 해당 노드의 자식 노드가 가진 값보다 크거나 작음 - 완전 이진 트리 형태를 가짐
* 데이터를 넣을 때 왼쪽부터 채워 넣음
힙과 이진 탐색 트리 비교
공통점
- 힙과 이진 탐색 트리는 모두 이진 트리
차이점
- 힙은 각 노드의 값이 자식 노드보다 크거나 같음(Max Heap)
- 이진 탐색 트리는 왼쪽 자식 노드의 값이 가장 작고 그 다음 부모 노드, 그 다음 오른쪽 자식 노드 값이 가장 큼
- 힙은 이진 탐색 트리의 조건인 자식 노드에서 작은 값은 왼쪽, 큰 값은 오른쪽이라는 조건은 없음
왼쪽이 클 수도, 오른쪽이 클 수도 있다. - 이진 탐색 트리는 탐색을 위한 구조, 힙은 최대/최소 값 검색을 위한 구조 중 하나로 이해하면 된다.
동작
데이터 삽입
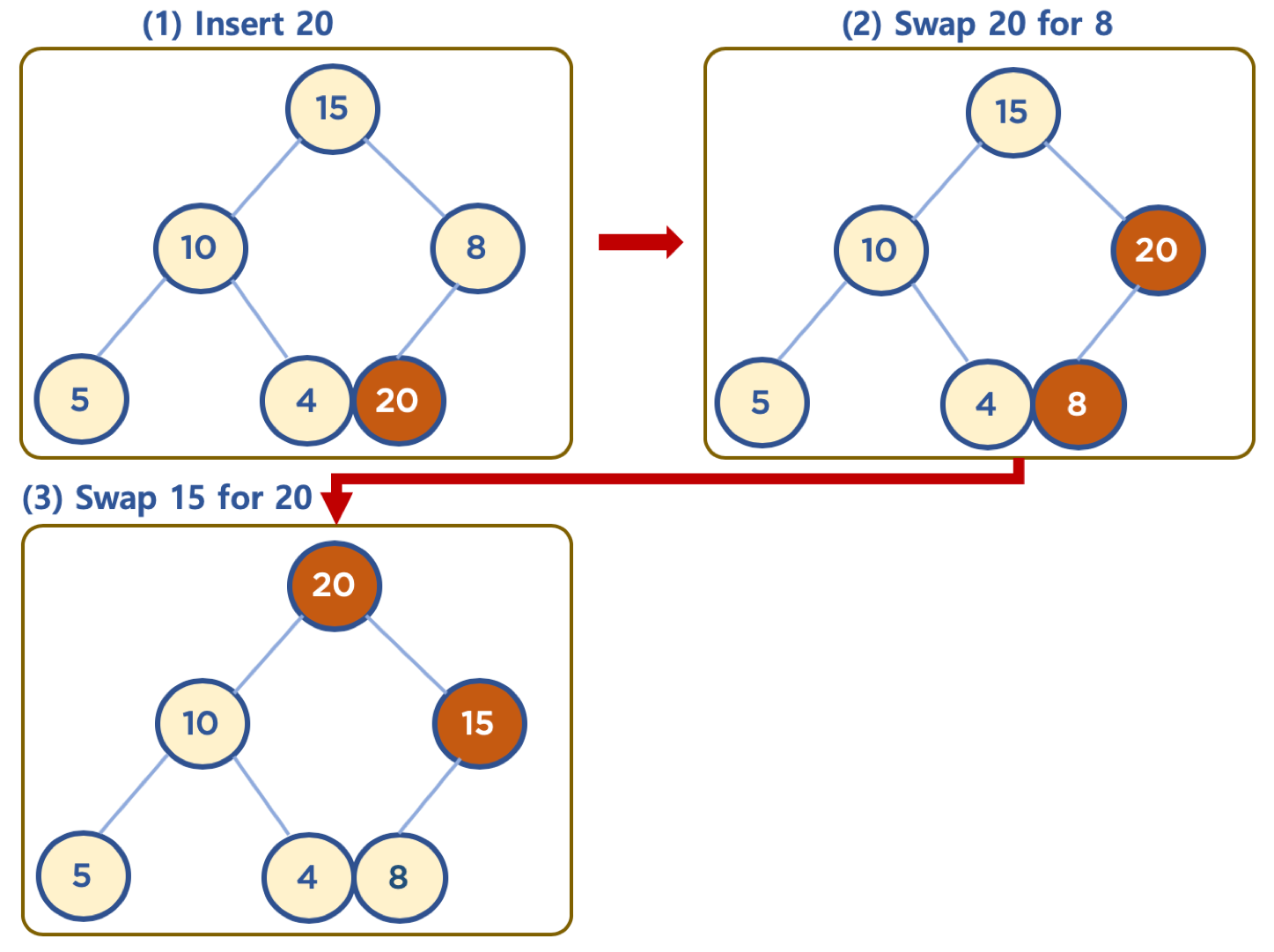
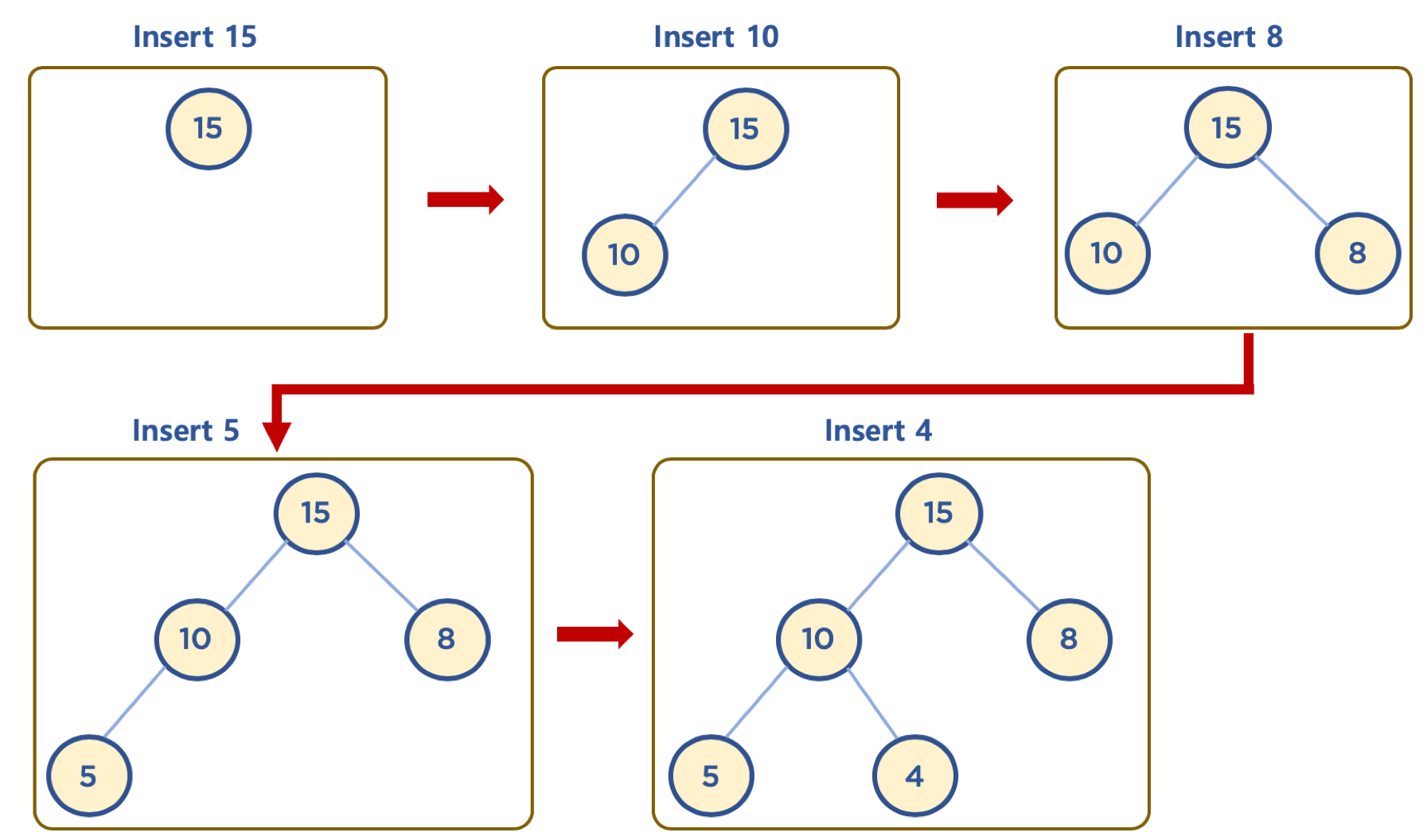
- 기본 동작으로 왼쪽 하단부터 채워짐
- 채워진 노드 위치에서, 부모 노드보다 값이 클 경우 부모 노드와 위치를 바꿔주는 작업을 반복 (swap)
데이터 삭제
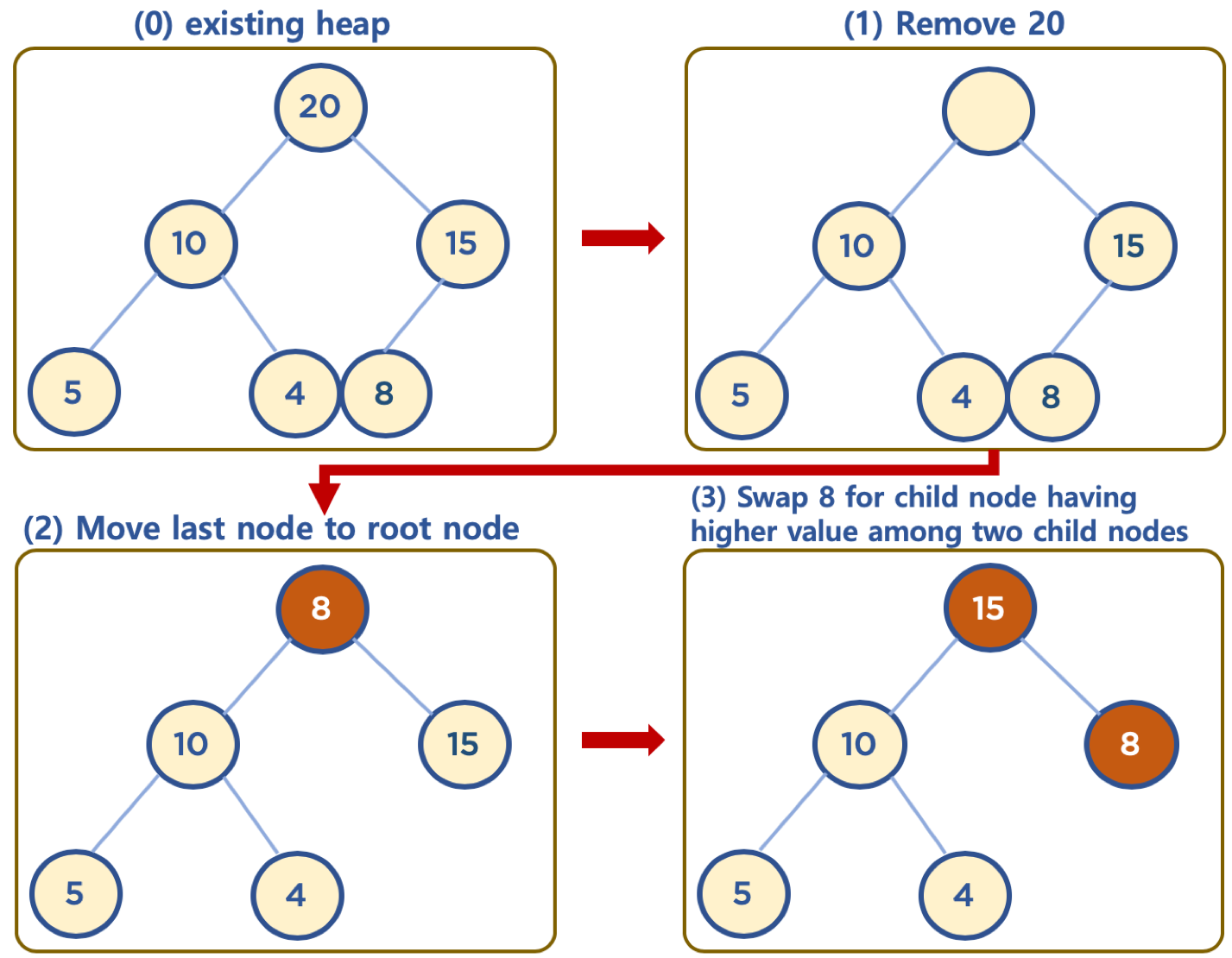
- 최상단 노드 (root 노드)를 삭제하는 것이 일반적 (최대값 또는 최소값을 root 노드에 놓고 바로 꺼내 쓸 수 있는 용도)
- 상단의 데이터 삭제 시, 가장 최하단부 왼쪽에 위치한 노드(가장 마지막에 추가한 노드)를 root 노드로 이동
- root 노드의 값이 child node 보다 작을 경우, root 노드의 child node 중 가장 큰 값을 가진 노드와
root 노드 위치를 바꿔주는 작업 반복 (swap)
구현
- 힙 구현 시 배열 자료구조 활용
- 배열은 인덱스가 0번부터지만, 힙 구현의 편의를 위해 root 노드 인덱스 번호를 1로 지정하면 구현이 좀 더 수월하다.
- 인덱스 구하는 방법
- 부모 노드 인덱스 번호(parent node's index): 자식 노드 인덱스 번호(child node's index) // 2
- 왼쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 번호(left child node's index): 부모 노드 인덱스 번호(parent node's index) * 2
- 오른쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 번호(right child node's index): 부모 노드 인덱스 번호(parent node's index) * 2 + 1
데이터 삽입
class Heap:
def __init__(self, data):
self.heap_arr = list()
self.heap_arr.append(None)
self.heap_arr.append(data) # heap = Heap(1), print(heap.heap_arr) -> [None, 1]
def move_up(self, inserted_idx): # 현재 인덱스의 노드가 부모 노드보다 큰지 여부 맞으면 True
if inserted_idx <= 1: # root node인 경우
return False
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
if self.heap_arr[inserted_idx] > self.heap_arr[parent_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
def insert(self, data):
if len(self.heap_arr) == 0:
self.heap_arr.append(None)
self.heap_arr.append(data)
return True
self.heap_arr.append(data) # 데이터 삽입은 끝. but, 비교 시작
inserted_idx = len(self.heap_arr) - 1 # 방금 넣은 데이터의 인덱스
while self.move_up(inserted_idx):
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
self.heap_arr[inserted_idx], self.heap_arr[parent_idx] = self.heap_arr[parent_idx], self.heap_arr[inserted_idx]
inserted_idx = parent_idx
return True
heap = Heap(15)
heap.insert(10)
heap.insert(8)
heap.insert(5)
heap.insert(4)
heap.insert(20)
print(heap.heap_arr) # [None, 20, 10, 15, 5, 4, 8]
데이터 삭제
# ... 윗부분 생략
def move_down(self, popped_idx):
left_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2
right_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2 + 1
# case 1. left_child_node == None
# case 2. left_child_node != None, right_child_node와 비교
# case 3-1. left_child_node와 right_child_node 비교 후 큰 값 리턴
# case 3-2. 3-1의 결과와 현재 값 비교
# case 1. 왼쪽 자식 노드도 없을 때
if left_child_popped_idx >= len(self.heap_arr): # 최대 idx+1 보다 같거나 크니까 존재하지 않음
return False # 바꿀 수 없음
# case 2. 오른쪽 자식 노드만 없을 때
elif right_child_popped_idx >= len(self.heap_arr):
if self.heap_arr[popped_idx] < self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
# case 3. 왼쪽, 오른쪽 자식 노드 모두 있을 때
else:
if self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx] > self.heap_arr[right_child_popped_idx]:
if self.heap_arr[popped_idx] < self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
else:
if self.heap_arr[popped_idx] < self.heap_arr[right_child_popped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
def pop(self):
if len(self.heap_arr) <= 1:
return None
returned_data = self.heap_arr[1]
self.heap_arr[1] = self.heap_arr[-1] # 맨 마지막 데이터를 root로 이동
del self.heap_arr[-1]
popped_idx = 1
while self.move_down(popped_idx):
left_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2
right_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2 + 1
if right_child_popped_idx >= len(self.heap_arr):
if self.heap_arr[popped_idx] < self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx]:
self.heap_arr[popped_idx], self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx] = self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx], self.heap_arr[popped_idx]
popped_idx = left_child_popped_idx
else:
if self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx] > self.heap_arr[right_child_popped_idx]:
if self.heap_arr[popped_idx] < self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx]:
self.heap_arr[popped_idx], self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx] = self.heap_arr[left_child_popped_idx], self.heap_arr[popped_idx]
popped_idx = left_child_popped_idx
else:
if self.heap_arr[popped_idx] < self.heap_arr[right_child_popped_idx]:
self.heap_arr[popped_idx], self.heap_arr[right_child_popped_idx] = self.heap_arr[right_child_popped_idx], self.heap_arr[popped_idx]
popped_idx = right_child_popped_idx
return returned_data
시간복잡도
depth(트리의 높이)를 h라고 표기한다면, n개의 노드를 가지는 heap에 데이터 삽입 또는 삭제 시,
최악의 경우 root 노드에서 leaf 노드까지 비교해야 하므로 h = log2n에 가까우므로, 시간복잡도는 O(logn)
* 참고: 빅오 표기법에서 logn에서 log의 밑은 10이 아니라 2
* 한번 실행 시 마다 50%의 실행할 수도 있는 명령을 제거. 즉, 50%의 실행시간을 단축
728x90
'자료구조알고리즘 > 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 동적 계획법(DP), 분할 정복(Divide and Conquer) (0) | 2023.04.13 |
|---|---|
| 재귀 활용 - 회문(팰린드롬), 더하기 조합 (0) | 2023.04.13 |
| Tree(트리) (0) | 2023.04.12 |
| Hash table(해시 테이블) - Chaining, Linear probing (0) | 2023.04.12 |
| 일차함수(직선)의 기울기 공식 (0) | 2022.12.19 |


